Velero for Kubernetes: Backup & Restore Stateful Workloads with AWS EBS Snapshots

This article is part of a series of blog posts on using Velero for Kubernetes backup, restore, migration & disaster recovery.
All articles in this series explore Velero in the context of AWS Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS).
Stay tuned as we publish more articles in the coming weeks & months. Here’s a sneak preview of what’s to come:
- An Introduction to Velero for Kubernetes Backup & Restore
- Velero for Kubernetes Backup: Install & Configure
- Backup & Restore Stateless Workloads with Velero for Kubernetes
- Velero for Kubernetes: Backup & Restore Stateful Workloads with AWS EBS Snapshots
- Velero for Kubernetes: Backup & Restore Stateful Workloads with Restic for Velero
- Monitoring Velero Kubernetes Backups & Automated Alerting for Backup Failures
Introduction
In the earlier post in this series, we explored how to backup & restore a stateless Nginx workload.
In this article, we will use Velero to backup & restore a stateful WordPress workload.
Install WordPress
First, let’s install WordPress as a Helm chart from Bitnami:
helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
helm install wordpress bitnami/wordpress \
--namespace wordpress --create-namespaceWait for it to spin up:
> kubectl get namespaces
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 10d
kube-node-lease Active 10d
kube-public Active 10d
kube-system Active 10d
velero Active 22h
wordpress Active 18h> kubectl get all --namespace wordpress
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/wordpress-7ff458b78c-bhmpf 1/1 Running 0 18h
pod/wordpress-mariadb-0 1/1 Running 0 18h
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/wordpress LoadBalancer 10.100.52.66 abcf13174045d4fde962cbf9b4be5d06-373553114.ap-south-1.elb.amazonaws.com 80:31079/TCP,443:32376/TCP 18h
service/wordpress-mariadb ClusterIP 10.100.196.201 <none> 3306/TCP 18h
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/wordpress 1/1 1 1 18h
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/wordpress-7ff458b78c 1 1 1 18h
NAME READY AGE
statefulset.apps/wordpress-mariadb 1/1 18hAdd Some State
Since this is supposed to be a stateful app, let’s add some state to the app.
Go to LOAD_BALANCER_URL/admin, login with the username user & add a blog post. Get the user’s password by running:
kubectl get secret wordpress \
--namespace wordpress \
-o jsonpath="{.data.wordpress-password}" \
| base64 --decodeBackup WordPress
Now backup the entire workload:
velero backup create wordpress \
--include-namespaces wordpress> velero backup describe wordpress
Name: wordpress
Namespace: velero
Labels: velero.io/storage-location=default
Annotations: velero.io/source-cluster-k8s-gitversion=v1.21.5-eks-bc4871b
velero.io/source-cluster-k8s-major-version=1
velero.io/source-cluster-k8s-minor-version=21+
Phase: Completed
Errors: 0
Warnings: 0
Namespaces:
Included: wordpress
Excluded: <none>
Resources:
Included: *
Excluded: <none>
Cluster-scoped: auto
Label selector: <none>
Storage Location: default
Velero-Native Snapshot PVs: auto
TTL: 720h0m0s
Hooks: <none>
Backup Format Version: 1.1.0
Started: 2022-01-22 22:09:05 +0530 IST
Completed: 2022-01-22 22:09:07 +0530 IST
Expiration: 2022-02-21 22:09:05 +0530 IST
Total items to be backed up: 48
Items backed up: 48
Velero-Native Snapshots: 2 of 2 snapshots completed successfully (specify --details for more information)Ah, it looks like our persistent volumes were backup up as EBS snapshots. Let’s take a look:
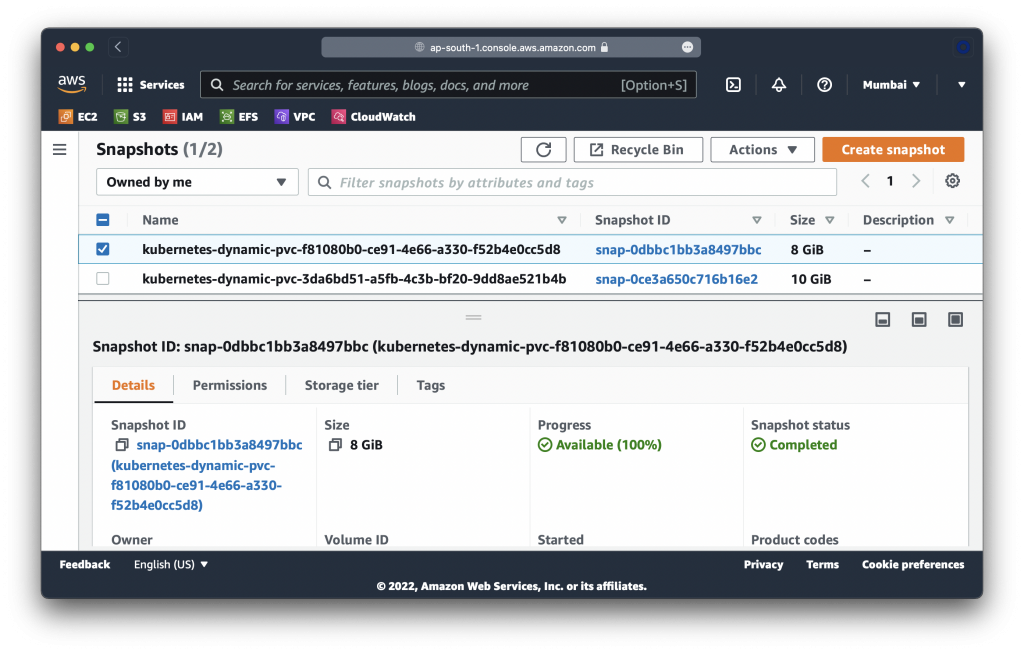
Excellent! Now let’s try deleting & recovering this workload!
Delete WordPress
Simulate a data loss by deleting WordPress:
> kubectl delete namespace wordpress
namespace "wordpress" deletedNotice the WordPress load balancer is gone too:
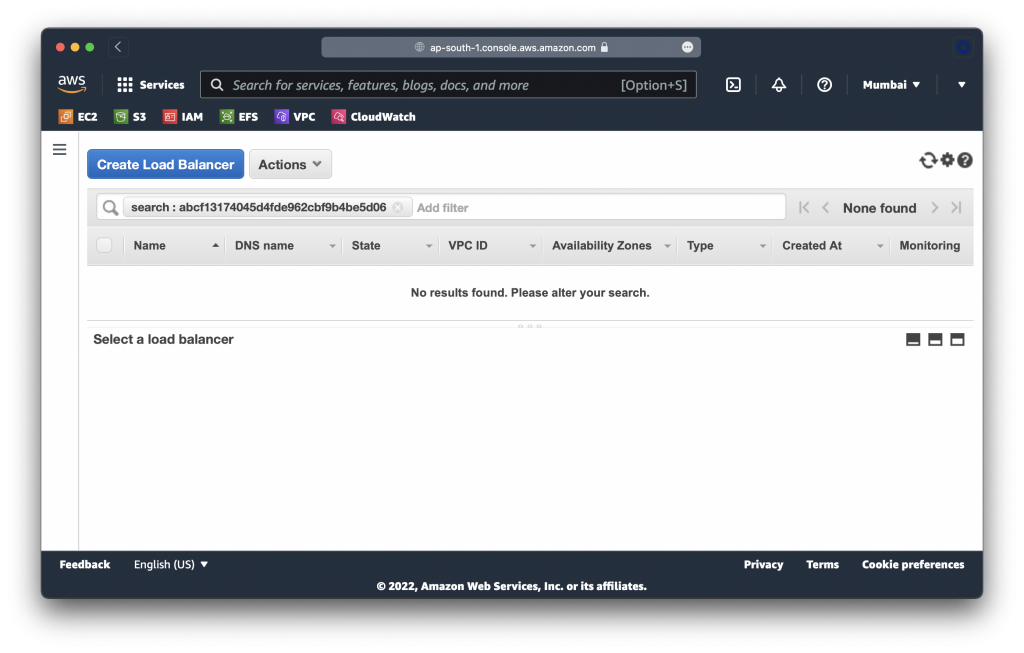
Restore WordPress
Let’s try a Velero restore from our WordPress backup:
> velero restore create wordpress --from-backup wordpress
Restore request "wordpress" submitted successfully.
Run `velero restore describe wordpress` or
`velero restore logs wordpress` for more details.> velero restore describe wordpress
Name: wordpress
Namespace: velero
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Phase: Completed
Total items to be restored: 26
Items restored: 26
Started: 2022-01-23 17:12:08 +0530 IST
Completed: 2022-01-23 17:12:10 +0530 IST
Backup: wordpress
Namespaces:
Included: all namespaces found in the backup
Excluded: <none>
Resources:
Included: *
Excluded: nodes, events, events.events.k8s.io, backups.velero.io, restores.velero.io, resticrepositories.velero.io
Cluster-scoped: auto
Namespace mappings: <none>
Label selector: <none>
Restore PVs: auto
Preserve Service NodePorts: autoAnd now, for the moment of truth: did we lose our data forever?
Find the new WordPress load balancer URL:
> kubectl get all --namespace wordpress
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/wordpress-7ff458b78c-bhmpf 1/1 Running 0 3m55s
pod/wordpress-mariadb-0 1/1 Running 0 3m55s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/wordpress LoadBalancer 10.100.3.69 a391b6489f3b04124a54350b4aa94ac0-450229137.ap-south-1.elb.amazonaws.com 80:30158/TCP,443:30719/TCP 3m55s
service/wordpress-mariadb ClusterIP 10.100.133.158 <none> 3306/TCP 3m55s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/wordpress 1/1 1 1 3m55s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/wordpress-7ff458b78c 1 1 1 3m55s
NAME READY AGE
statefulset.apps/wordpress-mariadb 1/1 3m55sIf you now visit the WordPress URL, you can see all the blog posts you added to your WordPress instance before it was deleted!
Conclusion
We have successfully backed up & restored a stateful Kubernetes workload using AWS EBS snapshots!
About the Author ✍🏻

Harish KM is a Principal DevOps Engineer at QloudX. 👨🏻💻
With over a decade of industry experience as everything from a full-stack engineer to a cloud architect, Harish has built many world-class solutions for clients around the world! 👷🏻♂️
With over 20 certifications in cloud (AWS, Azure, GCP), containers (Kubernetes, Docker) & DevOps (Terraform, Ansible, Jenkins), Harish is an expert in a multitude of technologies. 📚
These days, his focus is on the fascinating world of DevOps & how it can transform the way we do things! 🚀





