Automating Deployment of Compliance Frameworks in AWS Using Native IaC Tools: Part 4


Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Why Use Native AWS IaC for Security Automation?
- Key Components to Be Deployed
- Architecture Overview
- IaC Implementation Strategy
- CloudFormation or CDK Modules
- Sample templates
- Deployment Options
- Cost Estimation
- Real-World Lessons & Recommendations
- Packaging IaC Templates for Public/Enterprise Use
- Conclusion
- About the Author
Introduction
As cloud infrastructure grows in complexity, maintaining security and compliance manually becomes not just tedious, but risky. That’s where Infrastructure as Code (IaC) steps in — allowing organizations to codify security, compliance, and governance practices into repeatable templates.
This blog is the fourth installment in our AWS Compliance & Security series. Here’s how we’ve progressed so far:
- Blog 1 laid the foundation by setting up detection using AWS Config and Audit Manager.
- Blog 2 expanded this into an integrated security architecture, adding GuardDuty, Security Hub, Macie, and more.
- Blog 3 tackled automated remediation, enabling proactive enforcement of security policies.
Now in Blog 4, we’re bringing it all together with deployment automation. Our goal is to automate the setup of the entire compliance framework using AWS-native IaC tools — like CloudFormation, SSM Automation, and CodePipeline — ensuring the environment is secure by default and compliant at scale.
Whether you’re spinning up new environments, onboarding new AWS accounts, or enforcing baseline security in production, this blog will help you automate the entire stack — from detection to visualization — using modular, reusable templates.
Why Use Native AWS IaC for Security Automation?
In modern cloud-native environments, security is not just a post-deployment concern — it needs to be embedded into the infrastructure lifecycle. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) empowers organizations to codify their security posture and compliance checks, ensuring they are consistently enforced across environments.
Using AWS-native IaC tools like CloudFormation, CDK, and SSM Automation, we gain the following benefits:
- Security-First Deployments: Resources are provisioned with tightly scoped IAM permissions, encryption, tagging policies, and audit trails by default.
- Tight Integration with AWS Ecosystem: Native tools integrate seamlessly with Config, Security Hub, CloudWatch, Lambda, and more.
- Zero Third-Party Dependencies: Minimizes risk and complexity for security/compliance reviews.
- DevSecOps Alignment: Enables automated guardrails and faster compliance feedback in CI/CD pipelines.
- Repeatability and Scalability: Apply the same security standards across accounts and regions with minimal code changes.
Key Components to Be Deployed
This deployment will provision security and compliance services across detection, remediation, visualization, and auditing layers — as designed in Blog 1, 2, and 3. These components are grouped logically for modular deployment:
Detection Services
- AWS Config Rules: Includes managed rules (e.g., approved EC2 types, encrypted volumes) and custom rules (via Lambda).
- AWS Security Hub: Enable and configure CIS, Foundational Security Best Practices, and PCI standards.
- AWS GuardDuty: Enable across regions for threat detection.
- Amazon Macie: Scan S3 buckets for sensitive data.
- IAM Access Analyzer: Detect cross-account access or unused roles.
Remediation Components
- Lambda Functions: For dynamic actions like stopping instances, revoking keys, enforcing encryption.
- SSM Documents: For actions that don’t require code (e.g., tagging resources, configuration changes).
- EventBridge Rules: Trigger automation workflows on Security Hub/Config findings.
- IAM Roles and Policies: Least-privilege roles for Lambda, SSM, and EventBridge to execute automation securely.
Visualization Layer
- CloudWatch Alarms: Monitor remediation status, rule compliance, failed findings, and key metrics.
- CloudWatch Dashboards: Centralized security visibility (with filters by region/service).
Audit & Reporting
- AWS Audit Manager: Frameworks and custom controls enabled to collect evidence.
- S3 Buckets: Store audit reports and exported findings.
- SNS Topics: Notify on audit status or critical events (optional).
These components collectively form a scalable, production-grade security automation setup.
Architecture Overview
Architecture Layers:
- Source Control & CI/CD
- Source repo (AWS CodeCommit or GitHub) stores version-controlled CloudFormation templates or CDK stacks.
- A CodePipeline/CodeBuild pipeline triggers on changes or on-demand execution.
- Optional approval stages for high-impact changes like instance termination or access revocation.
- Deployment via CloudFormation/CDK
- Detection Stack: Deploys AWS Config Rules, enables Security Hub, GuardDuty, Macie, IAM Access Analyzer.
- Remediation Stack: Deploys EventBridge rules, Lambda functions, SSM documents, and IAM roles.
- Visualization Stack: Deploys CloudWatch dashboards and alarms tied to metrics and events.
- Audit Stack: Enables and configures AWS Audit Manager with scoped frameworks and evidence storage.
- Parameter Store / Tag-based Configuration
- Parameters (environment, region, severity threshold) fetched from SSM Parameter Store.
- Tag-based deployment strategies allow selective application of rules/remediations.
- Output and Logging
- CloudWatch Logs store automation history and error logs.
- SNS Topics can be integrated to notify DevSecOps teams on failed remediations or non-compliance spikes.
Architecture
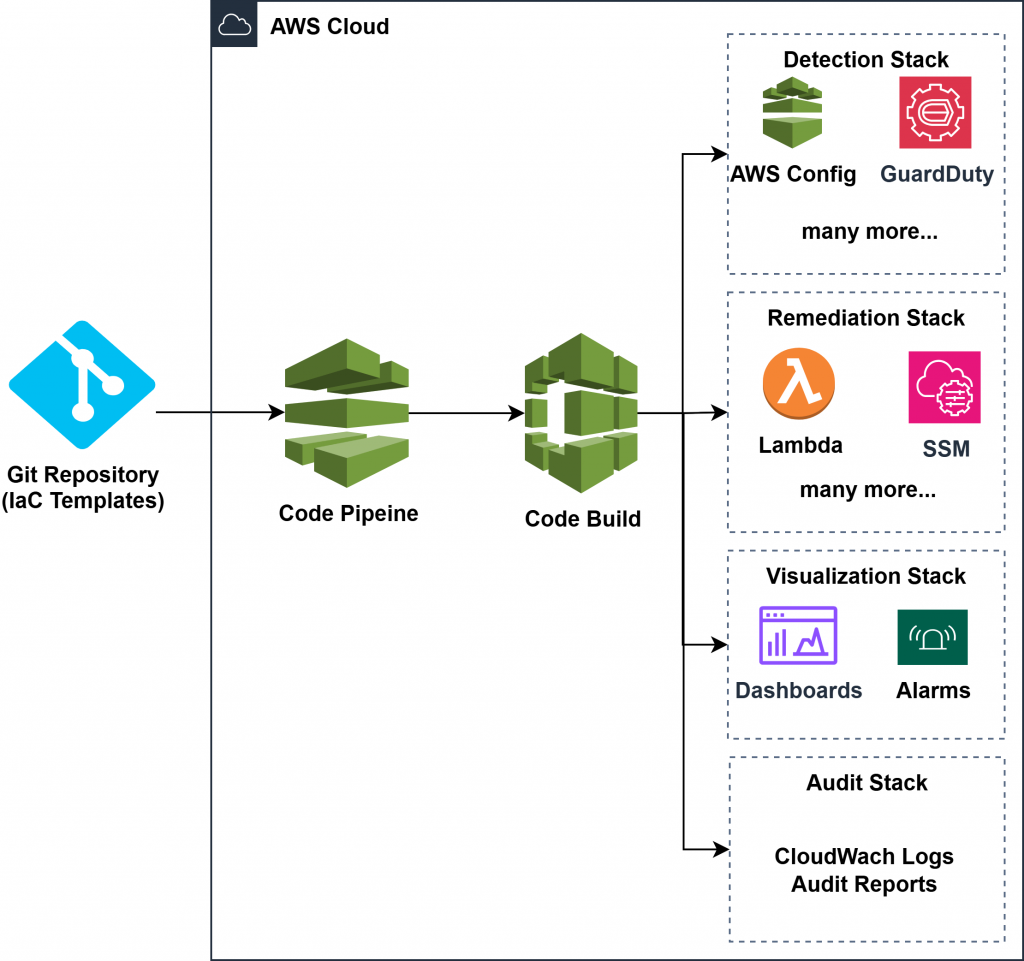
IaC Implementation Strategy
To maintain clarity, modularity, and ease of reuse, we structure the Infrastructure as Code (IaC) deployments into domain-based stacks:
Detection Stack
- Includes CloudFormation templates or CDK modules to:
- Enable AWS Config with global and regional rules.
- Activate Security Hub with desired standards like CIS, Foundational Best Practices, or PCI-DSS.
- Enable Amazon GuardDuty and configure findings publishing.
- Enable Amazon Macie with a default job to scan all S3 buckets.
- Turn on IAM Access Analyzer and enable logging.
Remediation Stack
- Automates creation of:
- Lambda Functions for dynamic remediations.
- SSM Documents for static or approval-based fixes.
- EventBridge Rules to trigger automation based on Security Hub or Config findings.
- IAM Roles & Policies for secure execution by automation components.
Visualization Stack
- Includes templates to:
- Create CloudWatch Dashboards (with filtering by region, service, compliance status).
- Deploy Alarms on failed remediations, high-severity findings, or disabled security controls.
- Enable log group retention policies and metrics exports to S3 (optional).
Design Considerations:
- Each stack can be deployed independently, enabling staged rollouts or service-by-service setup.
- Stack naming conventions (<env>-<service>-stack) and tagging (Project: Compliance, Team: Security) help with traceability.
- For organizations using CDK, each stack maps to a dedicated CDK construct for better reuse and testing.
CloudFormation or CDK Modules
To keep deployments consistent and scalable, use either CloudFormation templates or AWS CDK constructs for the modules.
Key Modules to Include
| Module | Description | Parameters |
| Config Rule Setup | Deploy AWS Config with rules for EC2 types, encryption, etc. | Rule IDs, scope, remediation |
| Security Hub Enablement | Turn on Security Hub and selected standards | Standards list, region |
| Remediation Lambda | Create Lambda functions tied to findings | Function name, runtime, role |
| SSM Document Creator | Deploy SSM Docs for automated fixes | Doc name, action, parameters |
| EventBridge Trigger | Set up finding pattern triggers | Source (Config, SecurityHub), severity |
| IAM Role for Automation | IAM roles for Lambda or SSM | Policy name, service trust |
| CloudWatch Alarms | Deploy alarms on metrics or logs | Thresholds, topic ARN |
| Dashboard Generator | Creates service-specific or region-wide dashboards | Widgets config, filters |
Sample templates
Sample Snippet: GuardDuty Member Management, SNS Notification, Config Recorder, Security Hub
Resources:
GuardDutyMember:
Type: AWS::GuardDuty::Member
Properties:
DetectorId: !Ref DetectorId
AccountId: 123456789012
Email: security@example.com
Status: EnabledResources:
SecuritySNSTopic:
Type: AWS::SNS::Topic
Properties:
DisplayName: SecurityAlerts
TopicName: security-alerts
SecuritySNSTopicSubscription:
Type: AWS::SNS::Subscription
Properties:
Endpoint: security-team@example.com
Protocol: email
TopicArn: !Ref SecuritySNSTopicResources:
ConfigRecorder:
Type: AWS::Config::ConfigurationRecorder
Properties:
Name: default
RoleARN: arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/aws-config-role
RecordingGroup:
AllSupported: true
IncludeGlobalResourceTypes: true
DeliveryChannel:
Type: AWS::Config::DeliveryChannel
Properties:
S3BucketName: your-config-bucket
ApprovedEC2TypesRule:
Type: AWS::Config::ConfigRule
Properties:
ConfigRuleName: approved-ec2-instance-types
Source:
Owner: AWS
SourceIdentifier: APPROVED_AMI_IDResources:
SecurityHubEnable:
Type: AWS::SecurityHub::Hub
Properties: {}
SecurityHubStandards:
Type: AWS::SecurityHub::StandardsSubscription
Properties:
StandardsArn: arn:aws:securityhub:::ruleset/cis-aws-foundations-benchmark/v/1.2.0Deployment Options
In this section, we describe both manual and automated deployment approaches to support various maturity levels of DevSecOps in organizations.
Manual Deployment
Ideal for testing, demos, or one-time deployments.
- Deploy CloudFormation templates through:
- AWS Console → CloudFormation → Upload YAML
- AWS CLI:
aws cloudformation deploy --template-file config-rules.yaml --stack-name config-rules --capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM
- Use Systems Manager (SSM) Automation documents manually from the SSM console.
Automated Deployment
Recommended for production environments to ensure repeatability, compliance, and auditability.
- CI/CD Pipeline with AWS CodePipeline + CodeCommit:
- Store IaC templates in CodeCommit
- Use CodePipeline stages:
- Source: Pull from CodeCommit/GitHub
- Build: Run
cfn-lint,cfn-nag, or policy tests - Deploy: Use CloudFormation or CDK deployment
- Optional: Add rollback plan using CloudFormation Change Sets
- Approval for Sensitive Actions:
- Add a manual approval step before deploying remediations like:
- Stopping EC2 instances
- Revoking IAM policies
- Deleting public access from S3
- AWS CodePipeline → Add Approval Stage using SNS/Email/Slack
- Add a manual approval step before deploying remediations like:
- Tracking and Rollback:
- CloudFormation provides version history
- Use Stack Policies to prevent accidental deletions
- Tag each stack version with metadata (e.g., security baseline version)
Cost Estimation
Monthly Cost Estimation (Based on Low/Medium Environment)
| Service | Monthly Estimate | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| AWS Config | $20–$30 | Based on 50–100 config items |
| Security Hub | $10–$15 | Basic standards (CIS, FSBP) |
| GuardDuty | $15–$25 | Includes VPC/DNS/S3 log analysis |
| Macie | $5–$10 | Scanning select buckets (partial scan) |
| IAM Analyzer | Free | Native service, no direct cost |
| Lambda | <$1 | Based on 1000 executions/month |
| SSM Automation | <$5 | Based on document executions |
| CloudWatch Logs | $3–$10 | For rule evaluations, alarms, dashboards |
| QuickSight | $9–$18 | Standard Edition per user |
Total Monthly Estimate: ~$75–$120
You can monitor actual cost via AWS Cost Explorer and set CloudWatch Billing Alarms.
Real-World Lessons & Recommendations
Based on real implementation feedback and AWS Well-Architected practices:
- Parameterize Everything:
- Use
ParametersandMappingsin CloudFormation to support multi-region, multi-account deployment
- Use
- Test Before Enforcing:
- Validate SSM Documents and Lambda functions using staging resources before enabling automation
- Tag Resources Consistently:
- Tag resources for ownership, environment, and compliance
- Helps in cleanup, cost analysis, and dashboards
- Avoid Direct Auto-Remediation in Production:
- Always prefer notification + approval + remediation chain
- Prevents unintended downtime or privilege revocation
- Include Alarms:
- Set CloudWatch Alarms for remediation failures, Lambda errors, or too many remediation retries
Packaging IaC Templates for Public/Enterprise Use
Recommended Folder Structure
To make your templates usable, modular, and enterprise-ready, use a GitHub-like layout:
aws-compliance-automation/
│
├── README.md
├── LICENSE
├── .gitignore
│
├── detection-stack/
│ ├── config-rules.yaml
│ ├── security-hub-enable.yaml
│ ├── guardduty-enable.yaml
│ ├── macie-enable.yaml
│ └── iam-access-analyzer.yaml
│
├── remediation-stack/
│ ├── lambda-remediations/
│ │ ├── ec2-stop-unapproved.py
│ │ └── kms-disable-key.py
│ ├── ssm-documents/
│ │ ├── tag-resources.json
│ │ └── enforce-encryption.json
│ ├── eventbridge-rules.yaml
│ └── iam-roles.yaml
│
├── visualization-stack/
│ ├── cloudwatch-dashboard.json
│ └── cloudwatch-alarms.yaml
│
├── audit-stack/
│ ├── audit-manager-enable.yaml
│ └── audit-s3-logging.yaml
│
└── utils/
├── parameters.env
├── tagging-policy.yaml
└── deploy.sh
Conclusion
By automating the provisioning of detection, remediation, and observability pipelines using AWS-native IaC tools, organizations can:
- Reduce manual security efforts
- Improve speed of compliance adoption
- Increase consistency and traceability
The use of modular CloudFormation templates, combined with CI/CD and approval mechanisms, ensures these security practices are not just enforced—but done securely and at scale.
In the next post (Blog 5), we’ll explore AWS Security Lake to build a central observability platform for multi-source logs, threats, and compliance.
About the Author
Deepali Sonune is a DevOps engineer with 12+ years of industry experience. She has been developing high-performance DevOps solutions with stringent security and governance requirements in AWS for 9+ years. She also works with developers and IT to oversee code releases, combining an understanding of both engineering and programming.





